之前我们已经介绍了逻辑回归、神经网络等机器学习算法,今天来聊聊另一种非常常用的算法:Support Vector Machine(支持向量机)。
首先我们来回顾下逻辑回归问题。对于逻辑回归,预测函数如下,当z » 0时,h(x)≈1,当 z « 0时,h(x) ≈ 0.
 对于单个 example 的 cost function 如下:
对于单个 example 的 cost function 如下:

SVM
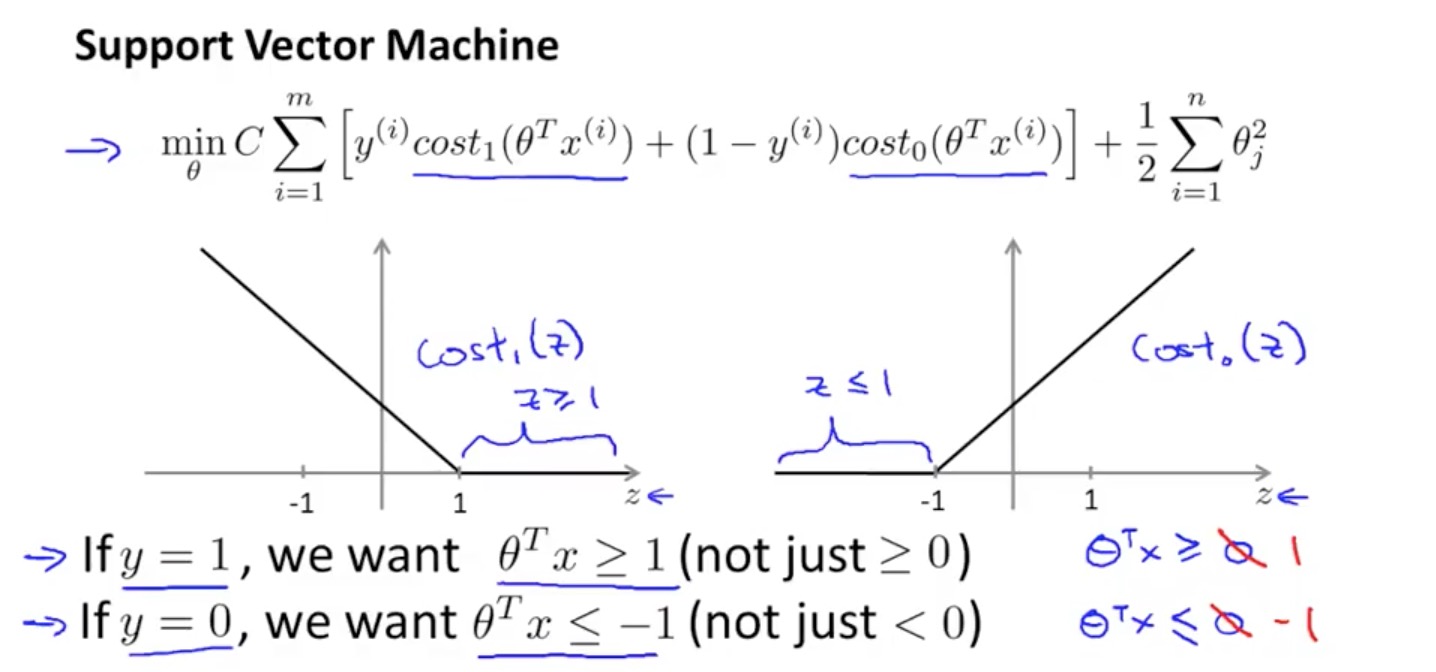
SVM 算法与普通逻辑回归算法的不同在于 cost function 的定义,cost function 不再是一条曲线,而是变成了直线。对于 y = 1 时的 cost function,当θ’x ≥ 1 时,cost function 为0,θ’x ≤ 1时,我们用一条直线替代原先的曲线,同理对于 y = 0时的 cost function,当θ’x ≤ -1时,cost function 为0,否则是一条直线。
逻辑回归算法的 cost function

SVM 算法的 cost function

需要注意:
- 由于 m (example count)是常量,所以在 SVM 中习惯删掉
- SVM 中单个 example 的 cost function 为 cost1、cost2,即前面提到的两条相交的直线
- SVM 中 C = 1 / λ
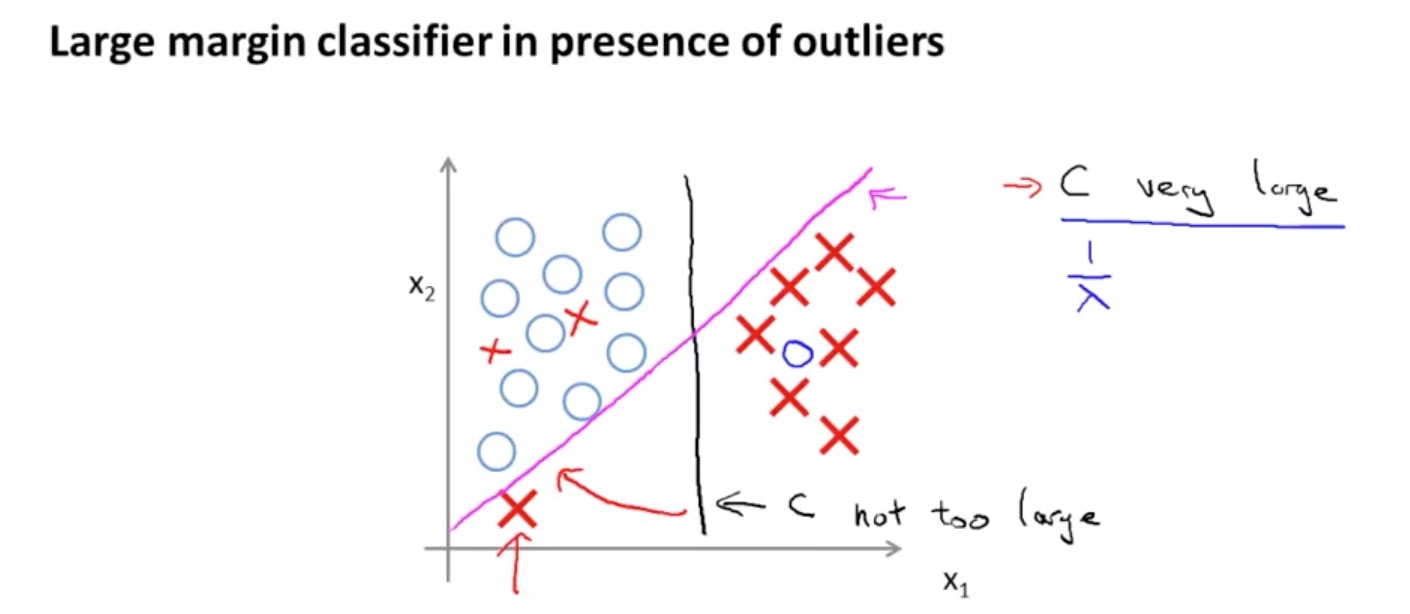
Large Margin Classifier
有些人习惯将 SVM 称作 Large Margin Classifier(大间距分类器),为什么这么说呢,因为在普通的逻辑回归算法中,当 y = 1 时,我们仅仅要求 θ’X ≥ 0,当 y = 0 时,要求 θ’X ≤ 0。但是 SVM 要求θ’X ≥ 1 /θ’X ≤ -1,即更大程度的区分度:

这里的 C 是个关键因子,考虑如下图所示,如果数据集中出现一个异常点,当 C 设置很大时(λ 很小),会发生 overfit 现象,所以我们需要谨慎的设置 C:
Mathematics Behind Large Margin Classification
在数学上,两个向量的内积公式如下:u’v = v’u = p⋅||u|| = u1⋅v1 + u2⋅v2。其中 p = length of projection of v onto the vector u。需要记住:If the angle between the lines for v and u is greater than 90 degrees, then the projection p will be negative.
现在再来看 SVM 的 cost function:
 最右侧的正则化公式可以变形为:
最右侧的正则化公式可以变形为:
 为了降低 cost function 的值,左侧的公式可变形为:
为了降低 cost function 的值,左侧的公式可变形为:

我们反过来看,为了降低 full cost function,右侧的正则化参数不能太大,即 Θ 不能太大,θ 较小,但是 p . ||Θ|| 又需要大,则 p 只能较大,即 X 映射到 Θ 上的长度较大,所以 decision boundaries 只能尽可能的远离正负样本集,这也正式 SVM 叫做 Large Margin Classifier 的原因。
Kernels
核函数可以让我们训练一些基于 SVM 的复杂的、非线性的分类器。那么什么是核函数呢?核函数本质是相似度函数,即度量两个向量的相似度,使用的比较多的一个核函数是 Gaussian Kernel(高斯核函数):
 可以看出,当 x ≈ l 时,f ≈ 1。当 x 远离 l 时,f ≈ 0。
可以看出,当 x ≈ l 时,f ≈ 1。当 x 远离 l 时,f ≈ 0。
那么 kernel 如何与 SVM 结合呢?
首先我们回顾下 SVM 的 cost function:

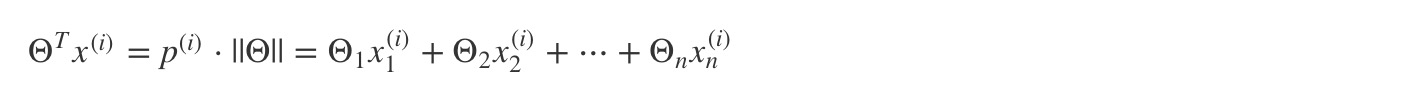 这里我们不再使用 Θ’ * X,而是使用 Θ’ * f,f 值是一个 m 维 vector,表明 x 与当前的 m 个训练样本集的 similarity, 具体如下:
这里我们不再使用 Θ’ * X,而是使用 Θ’ * f,f 值是一个 m 维 vector,表明 x 与当前的 m 个训练样本集的 similarity, 具体如下:
 所以,融合 SVM & Kernel 后的 cost function 如下:
所以,融合 SVM & Kernel 后的 cost function 如下:
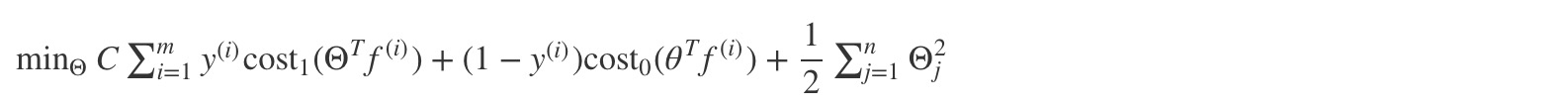
当然,kernel 不仅可以和 SVM 算法结合,也可以和 logistic regression 算法结合,不过由于 SVM 在cost function 上做的优化,所以 kernel & SVM 运行的效率更高,也更常用。
SVM & Kernels parameters optimize
SVM 中涉及到参数 C 的选择,kernel 涉及到 σ2的选择:

Multi-class classification 大部分的 SVM packages 已经内置了 multi-class classification function。如果要自己实现,原理其实跟之前提过的类似,如果有 K 种输出,需要训练 K 个 SVM,即训练出 K 个 Θ.
Logistic regression vs SVMs vs Neural Network
ML 算法的选择主要考虑两个点,m(number of training examples) & n(number of features)
- If n is large (relative to m), then use logistic regression, or SVM without a kernel (the “linear kernel”)
- If n is small and m is intermediate, then use SVM with a Gaussian Kernel
- If n is small and m is large, then manually create/add more features, then use logistic regression or SVM without a kernel.
总结:
- Neural Network 适用于上述所有场景,但是 Neural Network 有自己的缺点:训练速度慢
- logistic regression 与 SVM without a kernel 的适用场景是一致的。以及当 m 较大时,SVM with a kernel 性能会很差
- 但是,对于大多数情况来说,核心的问题仍然在于你有多少 data,多少 features
参考资料
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/resources/Es9Qo
